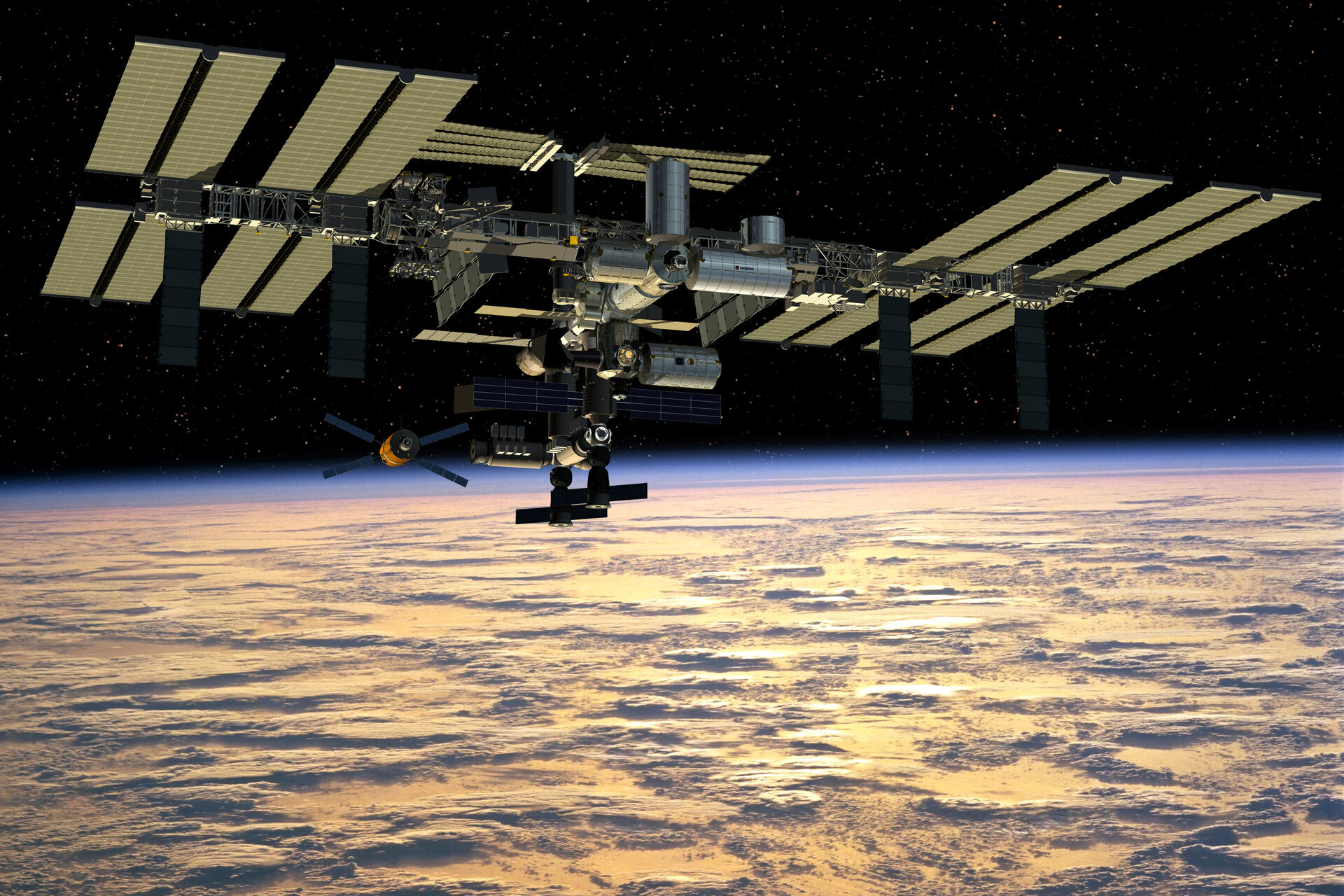
The International Space Station (ISS) stands as one of humanity's most remarkable achievements in space exploration, symbolizing global cooperation and scientific progress. Orbiting Earth at an altitude of approximately 400 kilometers, the ISS serves as a hub for groundbreaking research and technological innovation. This floating laboratory has become a testament to what can be accomplished when nations unite toward a common goal.
Since its inception in 1998, the ISS has captured the imagination of people worldwide. It represents not only a marvel of engineering but also a beacon of hope for future space exploration. The station's ability to host astronauts from various countries underscores its role in fostering international collaboration and advancing our understanding of space.
As we delve into this comprehensive guide, you will discover the history, significance, and future prospects of the International Space Station. Whether you're a space enthusiast, a student, or simply curious about humanity's ventures beyond Earth, this article offers valuable insights into one of the most ambitious projects ever undertaken.
Read also:Mavericks Vs Pacers A Deep Dive Into The Rivalry Game Analysis And Key Players
Table of Contents
- History of the International Space Station
- Construction and Assembly
- Structure and Design
- Functions and Purpose
- Scientific Research on the ISS
- Life Aboard the ISS
- Challenges Faced by the ISS
- International Partners and Cooperation
- Future of the International Space Station
- Conclusion
History of the International Space Station
The concept of the International Space Station originated during the early 1980s when NASA proposed the idea of a permanently manned space station. However, it wasn't until 1993 that the project gained momentum, with the formation of a global partnership involving the United States, Russia, Europe, Japan, and Canada. This collaboration aimed to create a shared platform for scientific research and technological advancement.
Key Milestones in the ISS's Development
- 1998: Launch of Zarya, the first module of the ISS.
- 2000: Arrival of the first long-term crew aboard the station.
- 2011: Completion of the ISS's primary structure.
Throughout its development, the ISS has undergone numerous upgrades and expansions, making it one of the most complex engineering projects in history. According to NASA, the station has been visited by more than 250 people from 19 countries, underscoring its role as a symbol of international cooperation.
Construction and Assembly
Building the International Space Station required meticulous planning and coordination among multiple space agencies. The construction process spanned over a decade, involving dozens of spaceflights and intricate assembly procedures.
Steps in the Assembly Process
- Design and development of modular components.
- Transportation of modules via space shuttles and rockets.
- On-orbit assembly by astronauts during spacewalks.
Data from the European Space Agency reveals that the ISS weighs approximately 420 tons and spans the area of a football field. Its modular design allows for flexibility and future expansion, ensuring its relevance in the evolving landscape of space exploration.
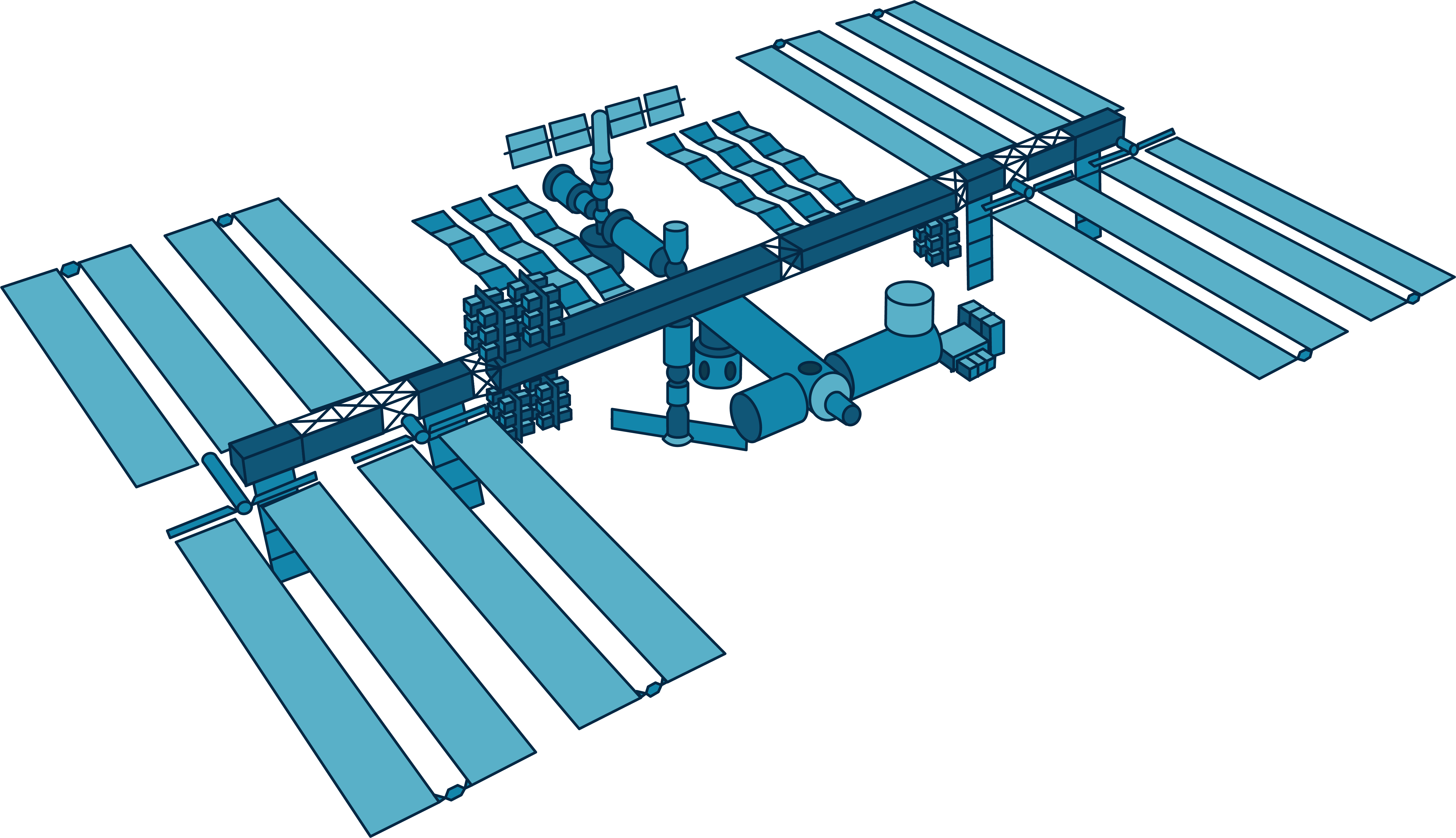
Structure and Design
The architecture of the International Space Station is both functional and innovative. Comprising multiple modules, solar arrays, and trusses, the station provides ample space for scientific experiments and daily operations.
Key Components of the ISS
- Modules: Habitable sections where astronauts live and work.
- Solar Arrays: Power generation units that supply electricity to the station.
- Trusses: Structural supports that connect various components.
The design of the ISS emphasizes efficiency and sustainability, with systems in place to recycle water and manage waste. These features are crucial for sustaining long-term human presence in space.
Read also:Leslie Bibb Explains Partner Sam Rockwellrsquos Surprise Lsquowhite Lotusrsquo Casting It Was Very Last Minute
Functions and Purpose
The primary purpose of the International Space Station is to serve as a platform for scientific research and technological development. Its unique microgravity environment enables experiments that cannot be conducted on Earth.
Areas of Focus
- Biology and biotechnology.
- Physical sciences and materials research.
- Earth observation and environmental studies.
Research conducted aboard the ISS has led to numerous breakthroughs, including advancements in medicine, materials science, and climate monitoring. For instance, studies on muscle atrophy in microgravity have provided insights into aging and rehabilitation therapies.
Scientific Research on the ISS
The International Space Station serves as a floating laboratory where cutting-edge experiments are carried out daily. These experiments span a wide range of disciplines, contributing to our understanding of both space and Earth-based phenomena.
Notable Experiments
- Investigations into plant growth in microgravity.
- Studies on the effects of radiation on living organisms.
- Development of new materials with unique properties.
According to a report by the National Academy of Sciences, research conducted on the ISS has resulted in over 2,000 scientific publications. These findings have practical applications in fields such as healthcare, agriculture, and technology.
Life Aboard the ISS
Living and working on the International Space Station presents unique challenges and opportunities for astronauts. The daily routine involves a combination of scientific experiments, maintenance tasks, and personal care.
Typical Day for an Astronaut
- Morning exercise to counteract muscle loss in microgravity.
- Conducting scheduled experiments and research activities.
- Meal times and relaxation periods.
Astronauts must adhere to strict protocols to ensure their health and safety while aboard the station. They also participate in regular communication with ground control and engage in outreach activities to educate the public about their work.
Challenges Faced by the ISS
Despite its successes, the International Space Station faces several challenges that threaten its long-term viability. These challenges include technical issues, funding constraints, and the need for continuous upgrades.
Common Challenges
- Micro-meteoroid and debris impacts.
- Aging infrastructure requiring repairs and replacements.
- Political and economic factors affecting funding.
Efforts are underway to address these challenges, including the development of new technologies and partnerships with private companies. These initiatives aim to extend the lifespan of the ISS and ensure its continued operation.
International Partners and Cooperation
The success of the International Space Station is largely due to the collaboration between its international partners. This partnership involves five space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), ESA (Europe), JAXA (Japan), and CSA (Canada).
Roles of Partner Agencies
- Providing modules and equipment for the station.
- Contributing to scientific research and experiments.
- Training astronauts and supporting mission operations.
This cooperative effort exemplifies the potential for global collaboration in addressing complex challenges. The ISS serves as a model for future space missions, demonstrating the power of unity in achieving common goals.
Future of the International Space Station
Looking ahead, the International Space Station is poised to play a critical role in shaping the future of space exploration. Plans are underway to extend its operational life beyond 2030 and explore new opportunities for commercial and scientific activities.
Future Initiatives
- Development of new modules and facilities.
- Expansion of private sector involvement in space research.
- Preparation for deep-space missions, including lunar and Martian exploration.
As humanity ventures further into space, the ISS will continue to serve as a vital stepping stone, providing valuable insights and experience for future missions.
Conclusion
The International Space Station represents a monumental achievement in human history, symbolizing the power of collaboration and innovation. From its inception to its current status as a hub for scientific discovery, the ISS has proven instrumental in advancing our understanding of space and its potential.
As we look to the future, the ISS will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of space exploration, inspiring generations to come. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and questions in the comments section below. Additionally, explore other articles on our site to deepen your knowledge of space-related topics.
Together, let us celebrate the achievements of the International Space Station and embrace the possibilities it offers for the future of humanity in space.