The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) plays a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape of the United States. As the monetary policymaking body of the Federal Reserve System, it influences interest rates, employment rates, and inflation. If you're interested in understanding how the U.S. economy operates, it's essential to learn about the FOMC's functions and decisions.
The FOMC is often discussed in financial circles, but many people still find its operations mysterious. By diving deeper into its structure, responsibilities, and impact on the economy, you'll gain valuable insights into the mechanisms that drive financial markets.
This article will provide an in-depth look at the FOMC, including its history, how it works, its influence on monetary policy, and its impact on global markets. Whether you're an investor, economist, or simply someone interested in finance, understanding the FOMC can help you make better financial decisions.
Read also:Brittany Fortinberry The Rising Star In The Entertainment World
Table of Contents
- Introduction to FOMC
- History of FOMC
- Structure of FOMC
- Role of FOMC
- FOMC Meeting Process
- Impact on Economy
- FOMC and Global Markets
- FOMC Statistics
- Criticisms of FOMC
- Future of FOMC
Introduction to FOMC
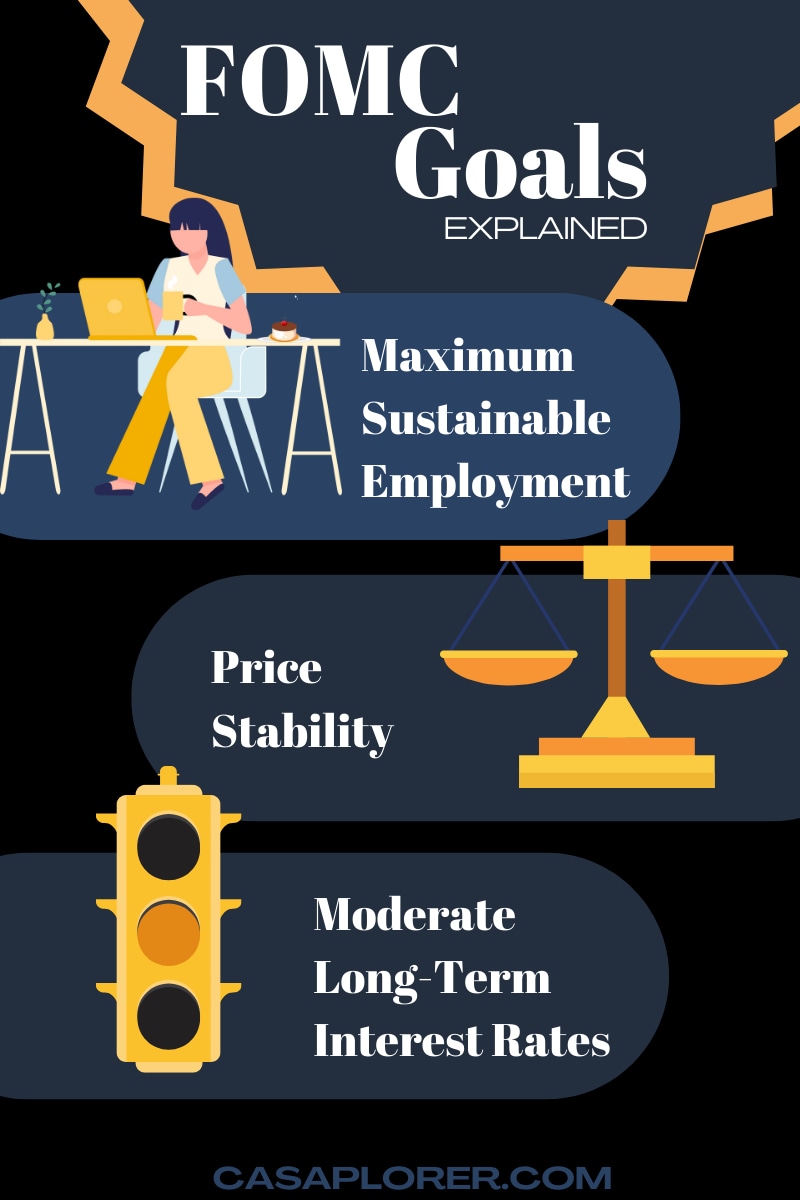
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is a critical component of the Federal Reserve System, responsible for making key decisions about monetary policy in the United States. Established in 1933, the FOMC operates under the Federal Reserve Act, with the primary goal of promoting maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates.
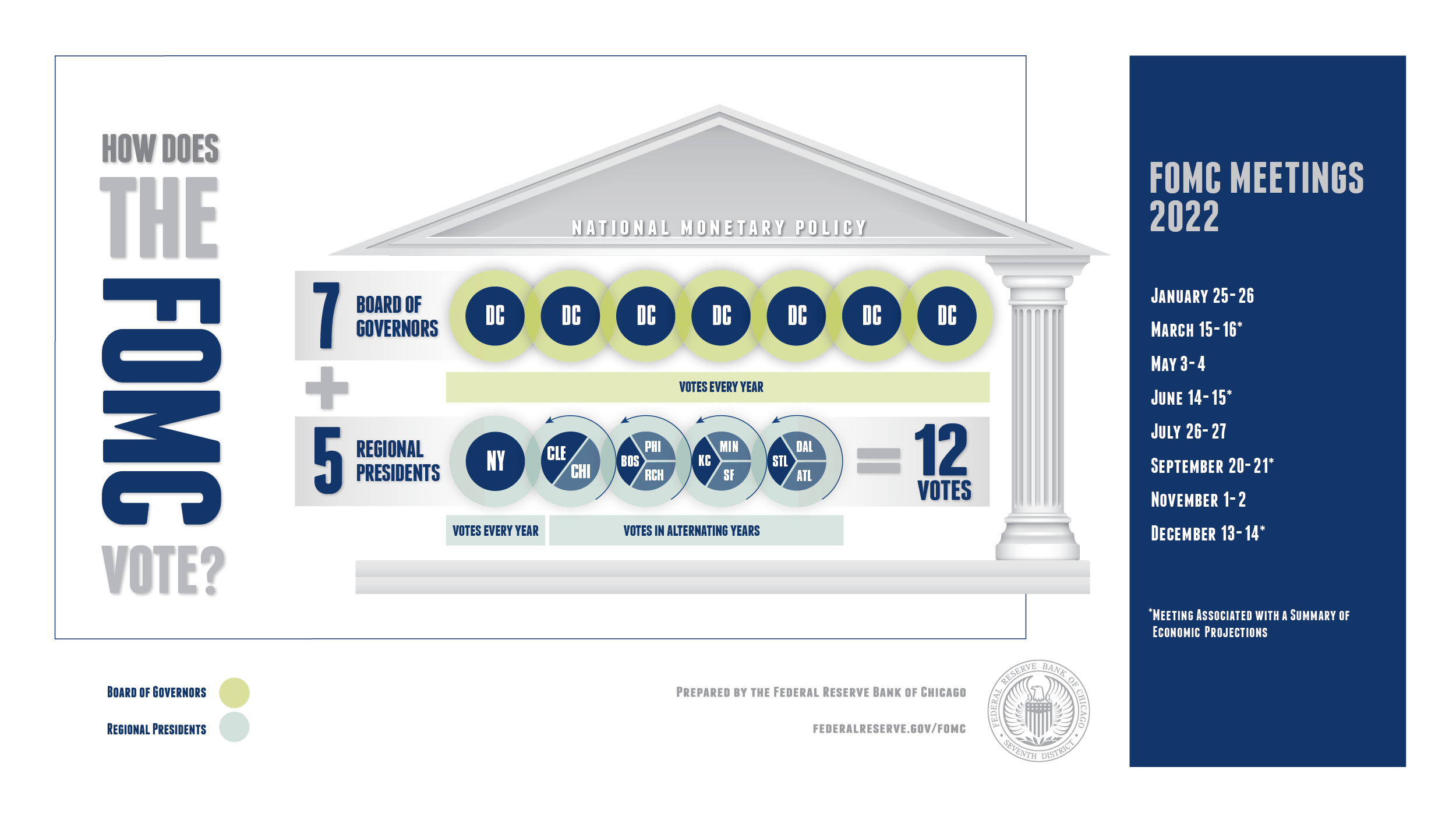
The FOMC consists of 12 members, including the seven members of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System and five of the 12 Reserve Bank presidents. This structure ensures a balance between centralized and decentralized decision-making, allowing for diverse perspectives in monetary policy formulation.
Why Is FOMC Important?
The FOMC is vital because its decisions directly affect the U.S. economy and, by extension, global financial markets. By setting the federal funds rate and conducting open market operations, the FOMC influences borrowing costs, investment levels, and overall economic activity.
History of FOMC
The Federal Open Market Committee was established in 1933 as part of the Banking Act of 1933, also known as the Glass-Steagall Act. Initially, the FOMC's role was limited, but its responsibilities expanded over time, especially during the post-World War II era. Today, the FOMC plays a central role in managing the U.S. economy and maintaining financial stability.
Key Milestones
- 1933: Establishment of the FOMC
- 1951: Treasury-Federal Reserve Accord, which gave the FOMC greater independence in setting monetary policy
- 1970s: Focus on controlling inflation during the stagflation period
- 2008: Active involvement in stabilizing the economy during the financial crisis
Structure of FOMC
The FOMC is composed of 12 members: the seven members of the Board of Governors and five Reserve Bank presidents. The president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York serves as a permanent voting member, while the remaining four positions rotate among the other Reserve Bank presidents.
Voting Members
The voting members of the FOMC include:
Read also:What Matters About The Indiana Pacers Play Compared To Expectations Pascal Siakam Allnba
- Chair of the Board of Governors
- Vice Chair of the Board of Governors
- President of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York
- Four Reserve Bank presidents who rotate annually
Role of FOMC
The primary role of the FOMC is to conduct monetary policy by influencing the availability and cost of money and credit in the economy. This is achieved through three main tools:
- Setting the target federal funds rate
- Conducting open market operations
- Adjusting reserve requirements
By using these tools, the FOMC aims to achieve its dual mandate of maximum employment and price stability.
Dual Mandate
The FOMC's dual mandate is to promote maximum employment and stable prices. This means that the committee must balance economic growth with inflation control, ensuring that the economy remains healthy without overheating.
FOMC Meeting Process
The FOMC holds eight regularly scheduled meetings per year, during which members discuss economic conditions and make decisions about monetary policy. The meetings typically last for two days and involve detailed presentations and discussions.
Key Steps in Meetings
- Economic data review
- Policy options discussion
- Voting on policy decisions
- Post-meeting statement release
Impact on Economy
The decisions made by the FOMC have a significant impact on the U.S. economy. Changes in the federal funds rate affect borrowing costs for consumers and businesses, influencing spending and investment decisions. Additionally, the FOMC's actions can influence inflation rates and employment levels.
Examples of Impact
For instance, during the 2008 financial crisis, the FOMC lowered interest rates to near zero to stimulate economic activity. Similarly, during periods of high inflation, the FOMC may raise interest rates to cool down the economy.
FOMC and Global Markets
The FOMC's decisions also have far-reaching effects on global financial markets. As the U.S. dollar is the world's primary reserve currency, changes in U.S. monetary policy can influence exchange rates, trade balances, and capital flows worldwide.
Global Market Reactions
When the FOMC announces a change in interest rates, global markets often respond quickly. For example, a rate hike may lead to a stronger dollar, affecting commodity prices and emerging market currencies.
FOMC Statistics
Data and statistics play a crucial role in the FOMC's decision-making process. The committee closely monitors economic indicators such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, and inflation to assess the health of the economy.
Key Statistics
- GDP growth rate
- Unemployment rate
- Inflation rate
- Federal funds rate
Criticisms of FOMC
While the FOMC plays a vital role in economic management, it is not without criticism. Some argue that the committee's decisions can lead to asset bubbles or excessive risk-taking in financial markets. Others question the transparency and accountability of the FOMC's operations.
Common Criticisms
- Lack of transparency
- Potential for political influence
- Risk of creating asset bubbles
Future of FOMC
As the global economy evolves, the role of the FOMC may continue to adapt. Challenges such as climate change, technological advancements, and shifting demographics may require new approaches to monetary policy. The FOMC must remain agile and forward-thinking to address these challenges effectively.
Looking Ahead
In the coming years, the FOMC will likely focus on maintaining economic stability while addressing emerging risks. By leveraging data-driven insights and fostering collaboration with global partners, the committee can continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of finance.
Conclusion
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is a cornerstone of the U.S. financial system, influencing monetary policy and economic outcomes. Understanding its structure, responsibilities, and impact is essential for anyone interested in finance or economics. As the global economy continues to evolve, the FOMC's role will remain critical in ensuring stability and growth.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and insights in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our website for more in-depth information on financial topics.
Data Sources: Federal Reserve Board, Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Commerce