Understanding Weather Tornadoes: A Comprehensive Guide To Nature's Fury
Mar 18 2025
Tornadoes are one of the most destructive weather phenomena on the planet, capable of causing immense damage within seconds. These powerful vortexes of wind can obliterate entire neighborhoods, uproot trees, and toss vehicles like toys. Understanding the science behind tornadoes, their formation, and how to stay safe during such events is crucial for anyone living in tornado-prone areas. This guide will provide you with an in-depth look into the world of tornadoes, covering everything from their formation to the latest research and safety tips.
Weather tornadoes are not just random occurrences; they are complex meteorological events that involve a combination of atmospheric conditions. Scientists have been studying these phenomena for decades, trying to understand their behavior and predict their paths. This knowledge is essential for developing early warning systems that can save lives. In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating world of tornadoes and equip you with the necessary information to stay safe.
This article is designed to help you understand the science behind tornadoes, their impact on communities, and the latest advancements in research. Whether you're a weather enthusiast or someone living in a tornado-prone area, this guide will provide valuable insights. Let's dive into the world of tornadoes and uncover the secrets behind these powerful storms.
Read also:Alec Baldwins Wife Snaps At Him On Camera In Shocking Video A Detailed Analysis
Table of Contents
- What Are Tornadoes?
- How Do Tornadoes Form?
- Tornado Classification and Scale
- Tornado-Prone Areas Around the World
- Tornado Season and Patterns
- Tornado Safety Tips
- Common Myths About Tornadoes
- The Latest in Tornado Research
- The Economic Impact of Tornadoes
- Conclusion: Preparing for the Future
What Are Tornadoes?
Tornadoes are violent rotating columns of air that extend from a thunderstorm to the ground. They are often referred to as "twisters" or "cyclones," although the term "cyclone" is more commonly used in other parts of the world for different weather phenomena. These powerful storms are characterized by their funnel-shaped clouds and can range in size from a few yards to over a mile wide.
Weather tornadoes are caused by a combination of factors, including warm moist air colliding with cool dry air, creating an unstable atmosphere. This instability leads to the formation of thunderstorms, which can sometimes spawn tornadoes. The rotation within the storm is a key factor in the development of a tornado.
Key Characteristics of Tornadoes
- Rotating wind speeds that can exceed 300 mph.
- Funnel-shaped clouds that extend from the base of a thunderstorm.
- Short duration, often lasting from a few seconds to several hours.
- Capable of causing catastrophic damage to structures and landscapes.
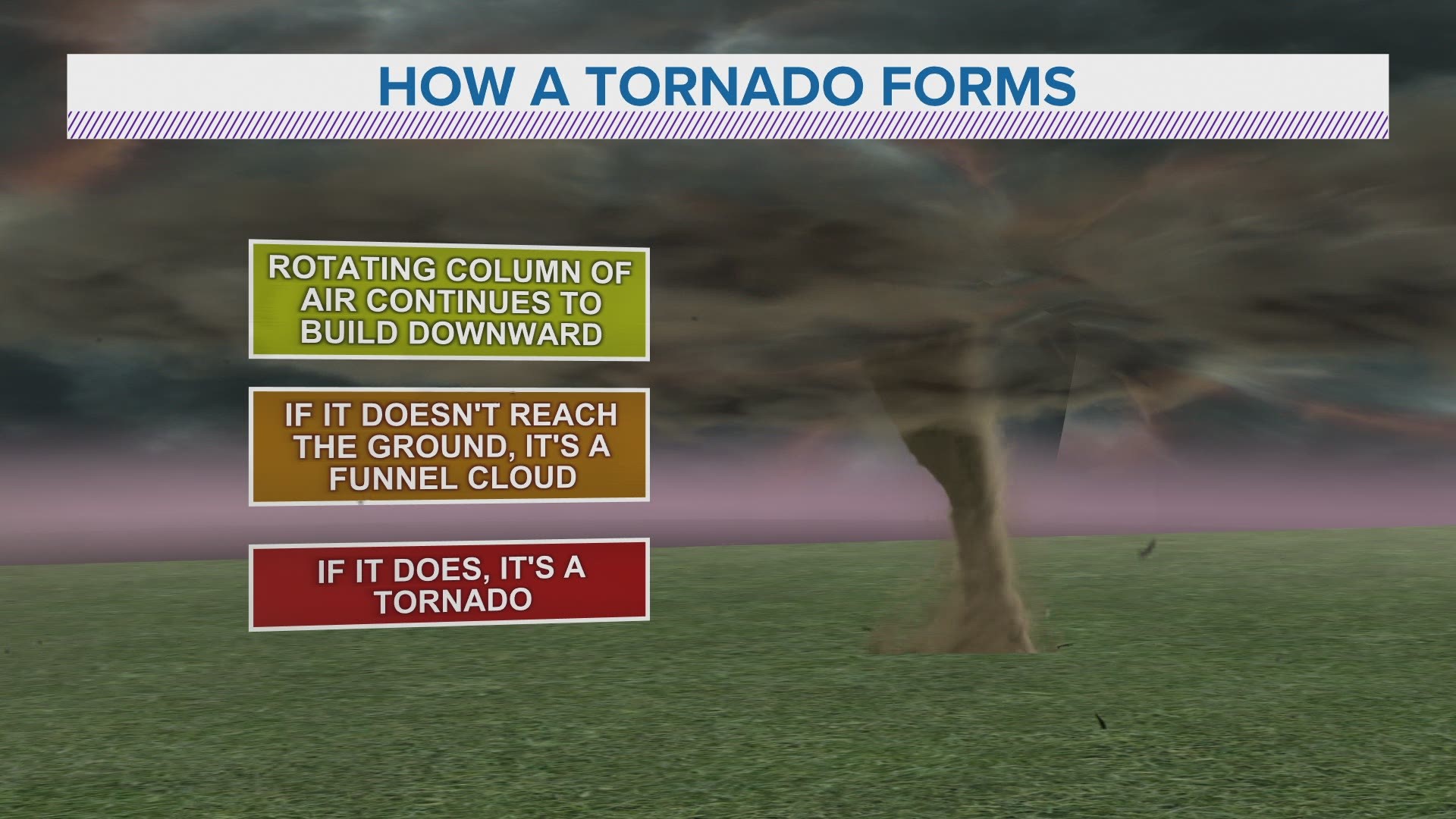
How Do Tornadoes Form?
The formation of a tornado is a complex process that involves several meteorological factors. It typically begins with the development of a supercell thunderstorm, which is a type of storm characterized by a deep, persistently rotating updraft known as a mesocyclone. The interaction of warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico with cooler, drier air from the north creates the perfect conditions for tornado formation.
As the warm air rises and meets the cooler air, it creates an area of instability. This instability, combined with wind shear (a change in wind direction and speed with height), can lead to the rotation of the storm. If the rotation extends to the ground, a tornado is born.
Steps in Tornado Formation
- Supercell Formation: A supercell thunderstorm develops with a rotating updraft.
- Wind Shear: Strong wind shear causes horizontal rotation in the atmosphere.
- Tilting Process: The horizontal rotation tilts vertically, creating a mesocyclone.
- Funnel Cloud: The mesocyclone tightens and stretches, forming a funnel cloud.
- Tornado Touchdown: The funnel cloud touches the ground, becoming a tornado.
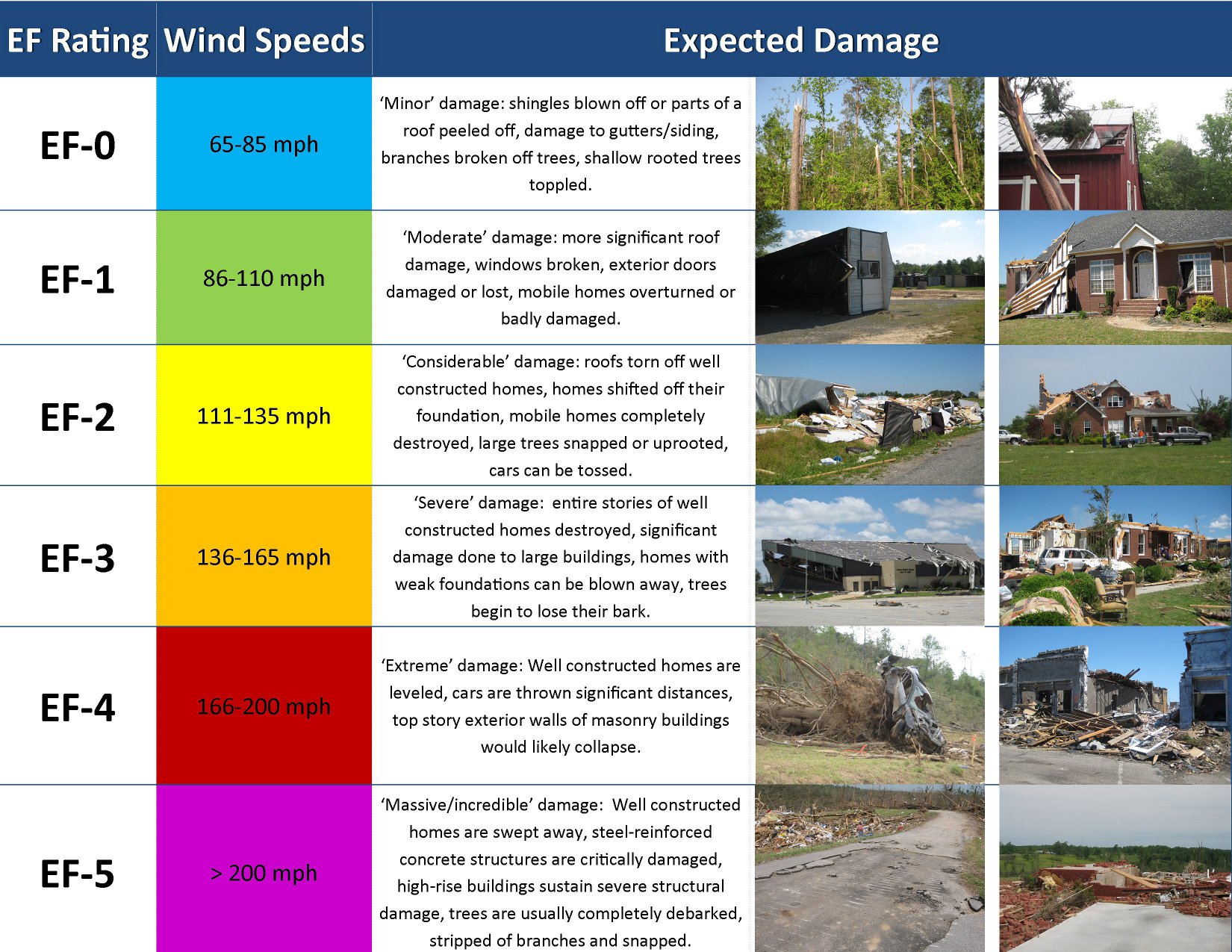
Tornado Classification and Scale
Tornadoes are classified based on their wind speed and the damage they cause. The Enhanced Fujita (EF) Scale is the most commonly used system for rating tornadoes. This scale ranges from EF0 (weakest) to EF5 (strongest), with each category representing a different level of destruction.
The EF Scale takes into account the type of damage caused to buildings and structures. For example, an EF1 tornado might cause minor damage to roofs and shatter windows, while an EF5 tornado can completely obliterate well-constructed homes.
Read also:Former Pittsburgh Steelers Quarterback Lands New Job On Deion Sanders Staff
EF Scale Categories
- EF0: Wind speeds of 65-85 mph, causing light damage.
- EF1: Wind speeds of 86-110 mph, causing moderate damage.
- EF2: Wind speeds of 111-135 mph, causing considerable damage.
- EF3: Wind speeds of 136-165 mph, causing severe damage.
- EF4: Wind speeds of 166-200 mph, causing devastating damage.
- EF5: Wind speeds over 200 mph, causing catastrophic damage.
Tornado-Prone Areas Around the World
While tornadoes can occur almost anywhere in the world, certain regions are more prone to these violent storms. The United States, particularly the area known as "Tornado Alley," experiences the highest frequency of tornadoes globally. This region includes states like Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, and Nebraska, where the perfect combination of atmospheric conditions often leads to tornado outbreaks.
Other countries, such as Canada, Australia, and parts of Europe, also experience tornadoes, though at a lower frequency. The unique geography and climate of these regions contribute to the formation of these storms.
Tornado Alley and Beyond
- Tornado Alley (USA): The epicenter of tornado activity in North America.
- Prairie Provinces (Canada): A significant number of tornadoes occur in Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba.
- Australia: The southeast region experiences frequent tornadoes, though they are generally weaker than those in the USA.
- Europe: Countries like Italy, France, and the UK occasionally experience tornadoes, though they are rare compared to the USA.
Tornado Season and Patterns
Tornado season refers to the time of year when tornadoes are most likely to occur. In the United States, tornado season typically peaks in the spring, from March to May, although tornadoes can occur at any time of the year. The exact timing and duration of tornado season can vary depending on geographic location and climate patterns.
Research has shown that tornado patterns are influenced by large-scale weather systems, such as El Niño and La Niña, which can affect the frequency and intensity of tornadoes in certain regions.
Tornado Season Trends
- Spring Peak: Most tornadoes occur in the spring, particularly in the central USA.
- Summer Activity: Tornado activity decreases in summer but can still occur in northern states.
- Fall and Winter: Secondary tornado seasons occur in the fall and winter, particularly in the southern USA.
Tornado Safety Tips
Staying safe during a tornado requires preparation and quick action. Knowing what to do before, during, and after a tornado can save lives. Emergency preparedness is crucial for anyone living in tornado-prone areas. Below are some essential safety tips to help you and your family stay safe during a tornado.
It’s important to have a tornado emergency plan in place and to practice it regularly. This includes identifying safe rooms in your home, having an emergency kit ready, and staying informed about weather conditions.
Essential Tornado Safety Tips
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather alerts and warnings through reliable sources.
- Identify Safe Rooms: Basements or interior rooms on the lowest floor are ideal.
- Emergency Kit: Prepare a kit with food, water, medications, and other essentials.
- Avoid Windows: Stay away from windows and glass doors during a tornado.
- Protect Yourself: Cover your head and body with blankets or pillows to protect against flying debris.
Common Myths About Tornadoes
There are many myths and misconceptions about tornadoes that can lead to dangerous behavior during a storm. Dispelling these myths is crucial for ensuring public safety. Below are some of the most common myths about tornadoes and the truth behind them.
For example, one common myth is that opening windows during a tornado will equalize pressure and prevent damage. In reality, this is not only ineffective but can also be dangerous, as it allows debris to enter the home.
Top Tornado Myths
- Opening Windows Helps: This is false; it can increase damage and risk.
- Tornadoes Only Occur in Flat Areas: Tornadoes can occur in any terrain.
- Highways Are Safe Shelters: Overpasses and highways are not safe during tornadoes.
The Latest in Tornado Research
Scientists are constantly working to improve our understanding of tornadoes and enhance prediction models. Advances in technology, such as Doppler radar and satellite imagery, have significantly improved our ability to detect and track tornadoes. Researchers are also exploring new methods for forecasting tornado outbreaks and improving warning systems.
Recent studies have focused on understanding the role of climate change in tornado frequency and intensity. While the exact relationship is still being investigated, some evidence suggests that climate change could lead to more intense storms in the future.
Key Advances in Tornado Research
- Doppler Radar: Enhanced radar systems provide better detection and tracking.
- Climate Studies: Investigating the impact of climate change on tornado patterns.
- Simulation Models: Developing advanced models to predict tornado behavior.
The Economic Impact of Tornadoes
Tornadoes can have a significant economic impact on affected communities. The cost of repairing and rebuilding damaged infrastructure can be staggering, with some tornado outbreaks resulting in billions of dollars in damages. In addition to property damage, tornadoes can disrupt local economies by destroying businesses and displacing residents.
Governments and organizations often provide financial assistance to affected communities, but the recovery process can take years. Understanding the economic impact of tornadoes is crucial for developing effective disaster response and recovery strategies.
Conclusion: Preparing for the Future
Tornadoes are powerful and unpredictable weather phenomena that require our attention and respect. By understanding the science behind tornadoes, their formation, and the latest research, we can better prepare for these storms and protect ourselves and our communities. Staying informed, following safety tips, and supporting research efforts are essential steps in mitigating the impact of tornadoes.
We encourage you to share this article with others and continue exploring the fascinating world of weather. For more information on tornadoes and other weather phenomena, check out our other articles and resources. Stay safe and informed!