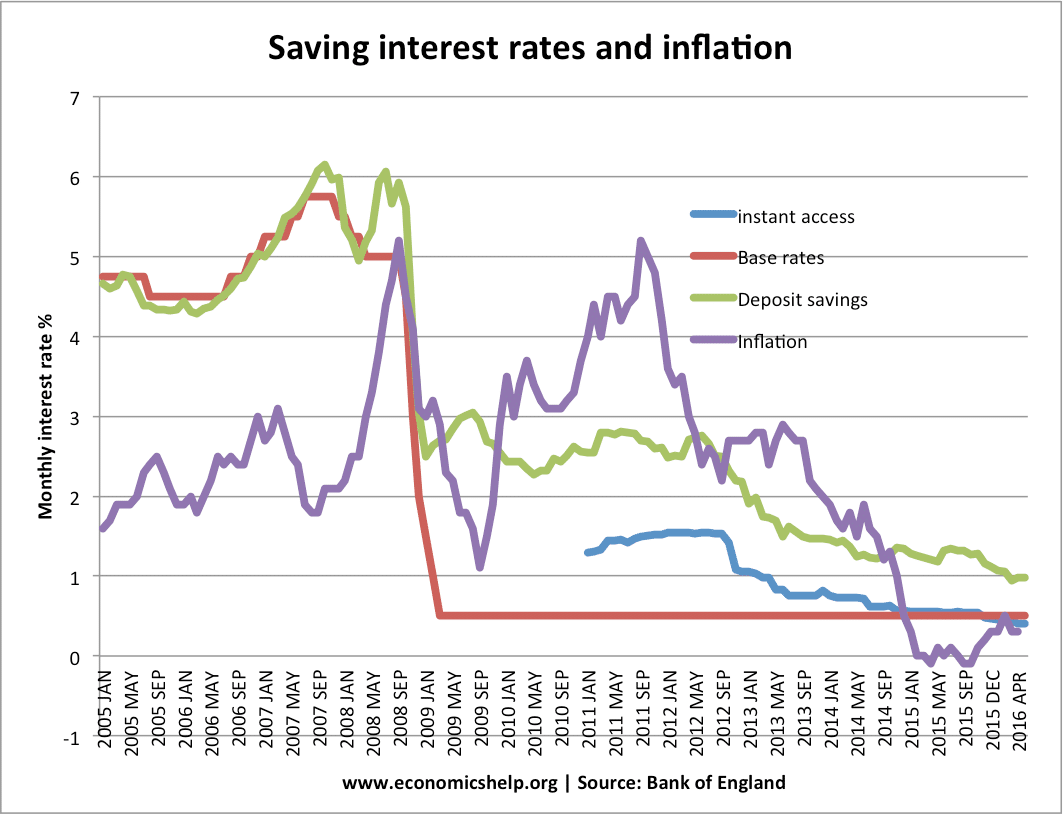
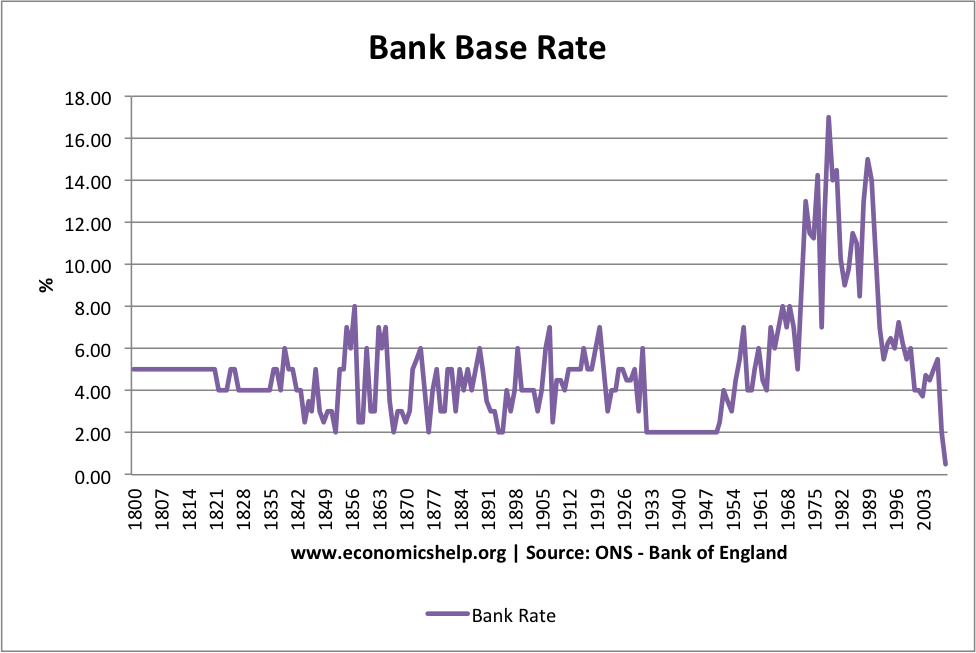
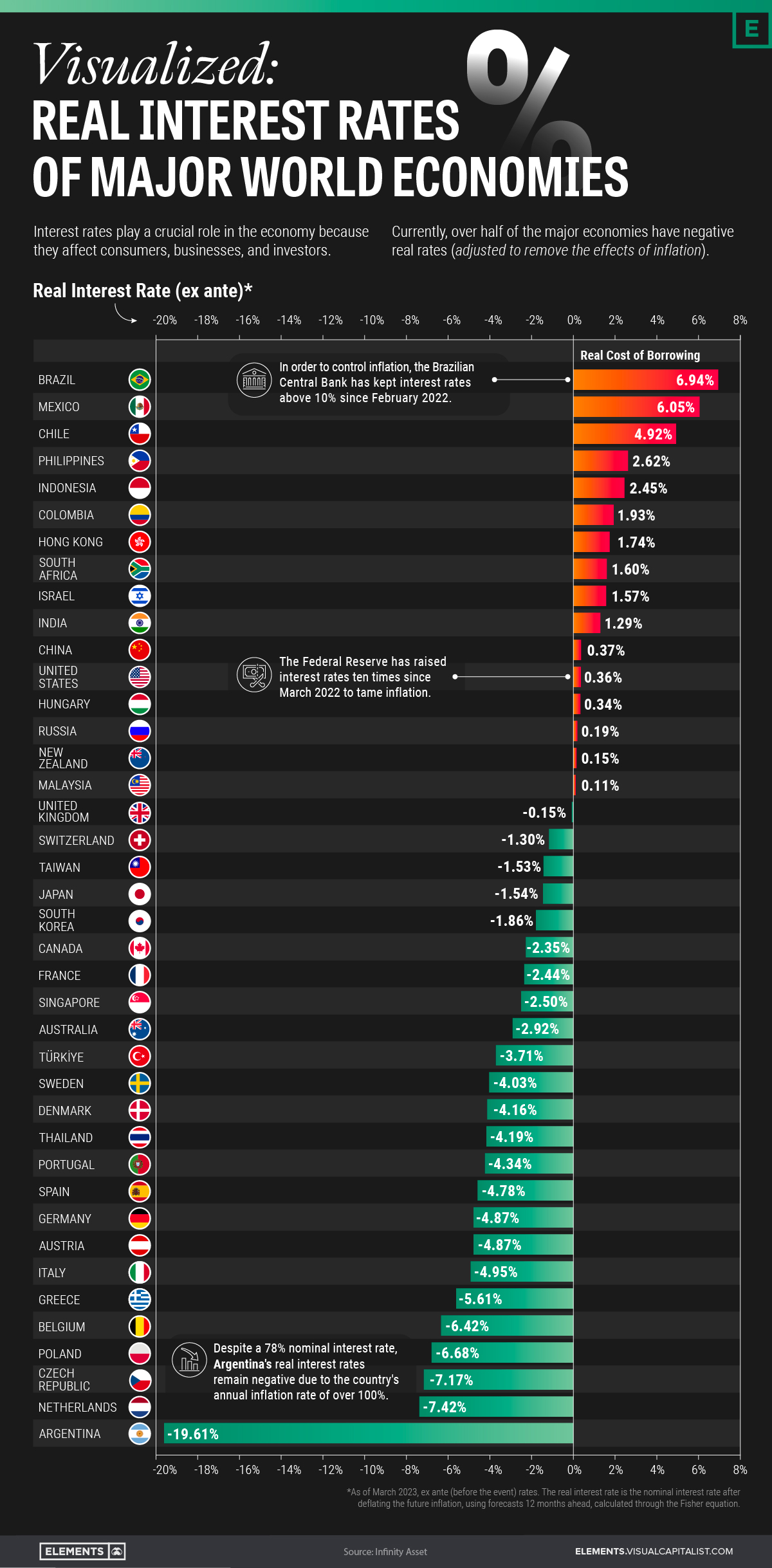
Interest rates are a critical component of the global economy, influencing everything from personal finances to national monetary policies. Whether you're saving, borrowing, or investing, understanding how interest rates work is essential. In this article, we'll delve into the intricacies of interest rates, exploring their impact on various aspects of financial life.
Interest rates are not just numbers; they represent the cost of borrowing money or the reward for saving it. They play a pivotal role in shaping economic growth, inflation, and consumer behavior. As we navigate through this guide, you'll gain a deeper understanding of how interest rates affect your financial decisions.
This article aims to provide you with valuable insights into interest rates, ensuring that you're well-equipped to make informed financial choices. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced investor, the information here will help you grasp the nuances of interest rates and their implications.
Read also:How To Watch The First Ncaa March Madness Games Schedule Start Time Channels Bracket And More
Table of Contents
- What Are Interest Rates?
- Types of Interest Rates
- Factors Affecting Interest Rates
- Importance of Interest Rates
- How Interest Rates Affect the Economy
- Central Banks and Interest Rates
- Interest Rates and Investing
- Historical Perspective of Interest Rates
- Future Trends in Interest Rates
- Conclusion
What Are Interest Rates?
Interest rates refer to the percentage charged or paid for the use of money. When you borrow money, you typically pay interest to the lender as compensation for the risk they take. Conversely, when you save money in a bank account, you earn interest as a reward for allowing the bank to use your funds.
Interest rates can vary widely depending on factors such as the type of loan, the creditworthiness of the borrower, and the prevailing economic conditions. Understanding the basics of interest rates is crucial for anyone looking to manage their finances effectively.
Components of Interest Rates
Interest rates consist of several components, including:
- Risk-Free Rate: The base rate, often tied to government bonds.
- Credit Risk Premium: Additional compensation for the risk of default.
- Inflation Premium: Adjustment for expected inflation.
Types of Interest Rates
There are various types of interest rates, each serving a different purpose in the financial system. Here are some of the most common types:
Nominal Interest Rates
Nominal interest rates are the stated interest rates that do not account for inflation. They represent the cost of borrowing or the return on savings before adjusting for inflation.
Real Interest Rates
Real interest rates adjust nominal rates for inflation, providing a more accurate picture of the cost of borrowing or the return on savings. Real interest rates are crucial for long-term financial planning.
Read also:Jason Aldean Has A New Dance Partner And Itrsquos Not His Wife Pic
Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates
Fixed interest rates remain constant throughout the life of a loan, while variable interest rates can fluctuate based on market conditions. Borrowers often prefer fixed rates for predictability, whereas variable rates may offer lower initial costs.
Factors Affecting Interest Rates
Interest rates are influenced by a variety of factors, including economic conditions, monetary policy, and global events. Here are some key factors:
- Economic Growth: Strong economic growth can lead to higher interest rates as demand for credit increases.
- Inflation: Rising inflation often prompts central banks to raise interest rates to control price increases.
- Monetary Policy: Central banks use interest rates as a tool to manage economic activity and inflation.
Global Influences
Global events, such as geopolitical tensions or changes in international trade, can also impact interest rates. For example, a financial crisis in one country may lead to increased demand for safe-haven assets, affecting global interest rates.
Importance of Interest Rates
Interest rates are vital for both individuals and businesses. They influence spending, saving, and investment decisions, ultimately shaping economic outcomes. Here's why interest rates matter:
- Consumer Behavior: Lower interest rates encourage borrowing and spending, while higher rates promote saving.
- Business Investment: Companies rely on interest rates to determine the cost of capital for expansion and projects.
- Government Policy: Central banks use interest rates to implement monetary policy and stabilize the economy.
Impact on Savings
For savers, interest rates determine the return on their investments. Higher rates mean greater rewards, incentivizing people to save more. Conversely, low rates may discourage saving in favor of spending or investing in higher-yielding assets.
How Interest Rates Affect the Economy
Interest rates have a profound impact on the economy, influencing everything from employment levels to inflation. Here's how:
Inflation Control
Raising interest rates can help control inflation by reducing consumer spending and borrowing. Conversely, lowering rates can stimulate economic growth during periods of stagnation.
Housing Market
Interest rates directly affect the housing market. Lower rates make mortgages more affordable, boosting demand for homes. Higher rates, on the other hand, can slow down the housing market as borrowing costs increase.
Employment
Businesses often rely on borrowing to expand operations and hire more employees. Interest rates play a critical role in determining the cost of such borrowing, impacting employment levels.
Central Banks and Interest Rates
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States or the European Central Bank, are responsible for setting interest rates. They use monetary policy tools to adjust rates based on economic conditions.
Monetary Policy Objectives
The primary objectives of central banks include maintaining price stability, promoting economic growth, and ensuring full employment. Interest rates are a key instrument in achieving these goals.
Tools Used by Central Banks
Central banks employ various tools to influence interest rates, including open market operations, reserve requirements, and discount rates. These tools help them manage liquidity and control economic activity.
Interest Rates and Investing
Interest rates significantly impact investment decisions. Investors consider rates when evaluating the potential returns on various asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate.
Impact on Bonds
Interest rates and bond prices have an inverse relationship. When rates rise, existing bond prices fall, and vice versa. This relationship is crucial for fixed-income investors.
Stock Market
Higher interest rates can negatively affect stock markets by increasing borrowing costs for companies. Conversely, lower rates may boost stock prices by making borrowing cheaper and encouraging expansion.
Historical Perspective of Interest Rates
Interest rates have fluctuated throughout history, reflecting changing economic conditions and policies. Examining historical trends can provide valuable insights into future movements.
Key Historical Events
Notable events, such as the Great Depression, the 1970s oil crisis, and the 2008 financial crisis, have all influenced interest rates. Understanding these events helps investors and policymakers anticipate future changes.
Long-Term Trends
Over the past few decades, interest rates have generally trended downward in many developed economies. This trend is attributed to factors such as globalization, technological advancements, and demographic shifts.
Future Trends in Interest Rates
Looking ahead, several factors could shape the future of interest rates. These include:
- Climate Change: As countries focus on sustainability, green finance may influence interest rate policies.
- Technological Innovation: Advances in technology could alter borrowing and lending practices, impacting rates.
- Demographics: Aging populations and changing workforce dynamics may affect savings and investment patterns.
Potential Challenges
Central banks face challenges in balancing economic growth with inflation control. Future developments in global trade, geopolitical tensions, and unforeseen crises could also influence interest rate decisions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, interest rates are a fundamental aspect of the financial system, affecting everything from personal savings to national economic policies. By understanding the factors that influence interest rates and their implications, you can make more informed financial decisions.
We encourage you to explore further resources and stay updated on economic developments. Share your thoughts in the comments below, and don't forget to check out our other articles for more insights into the world of finance.